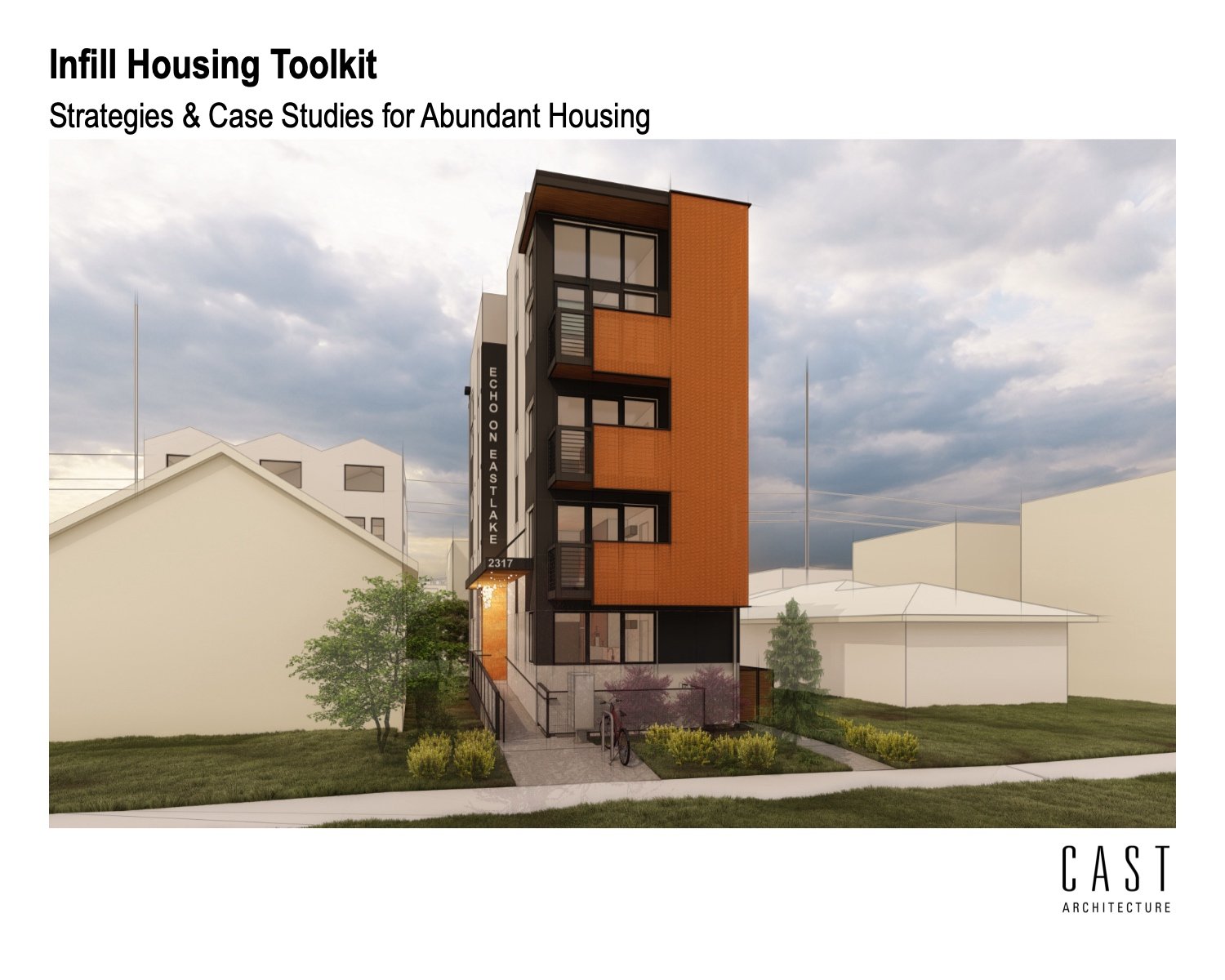
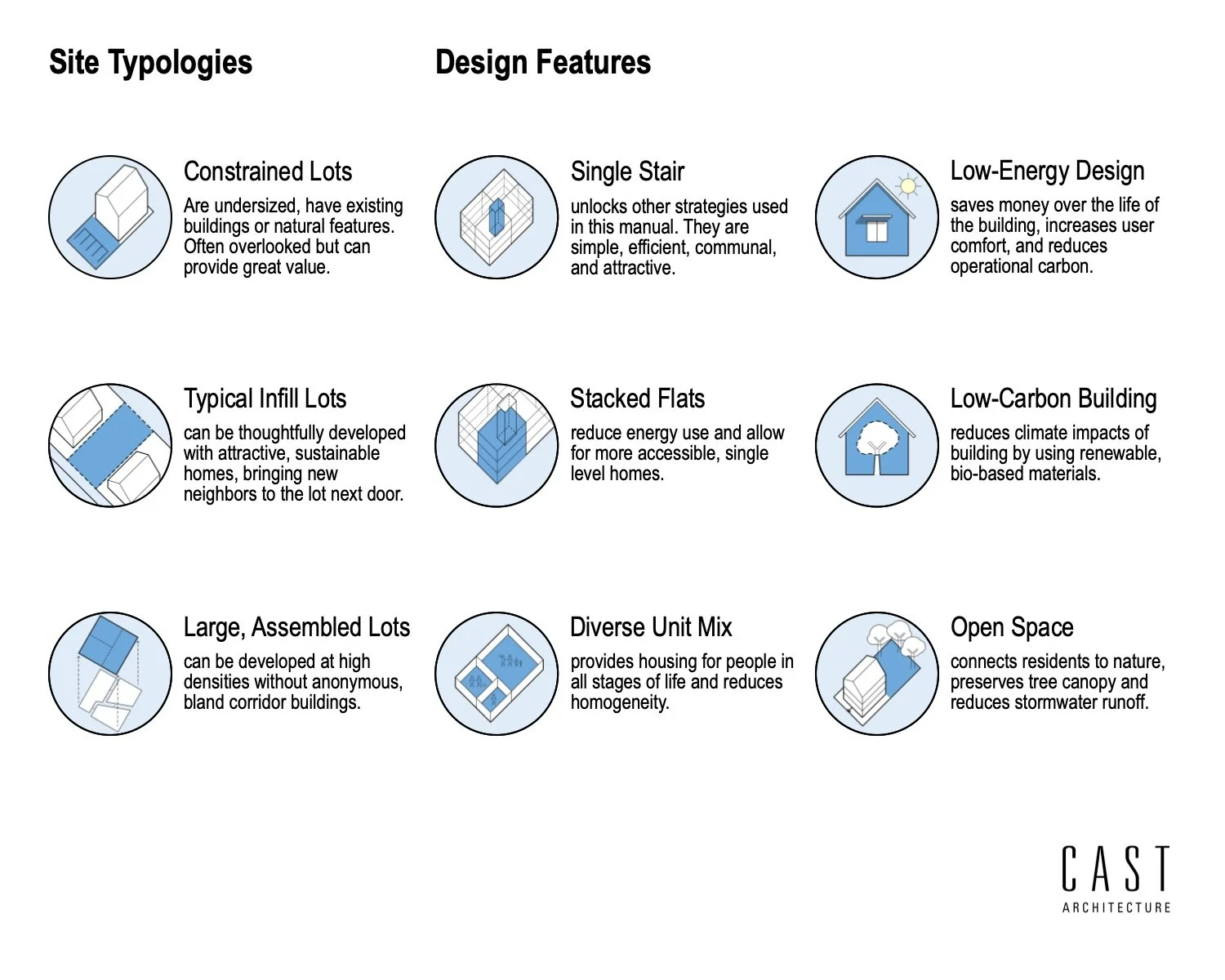
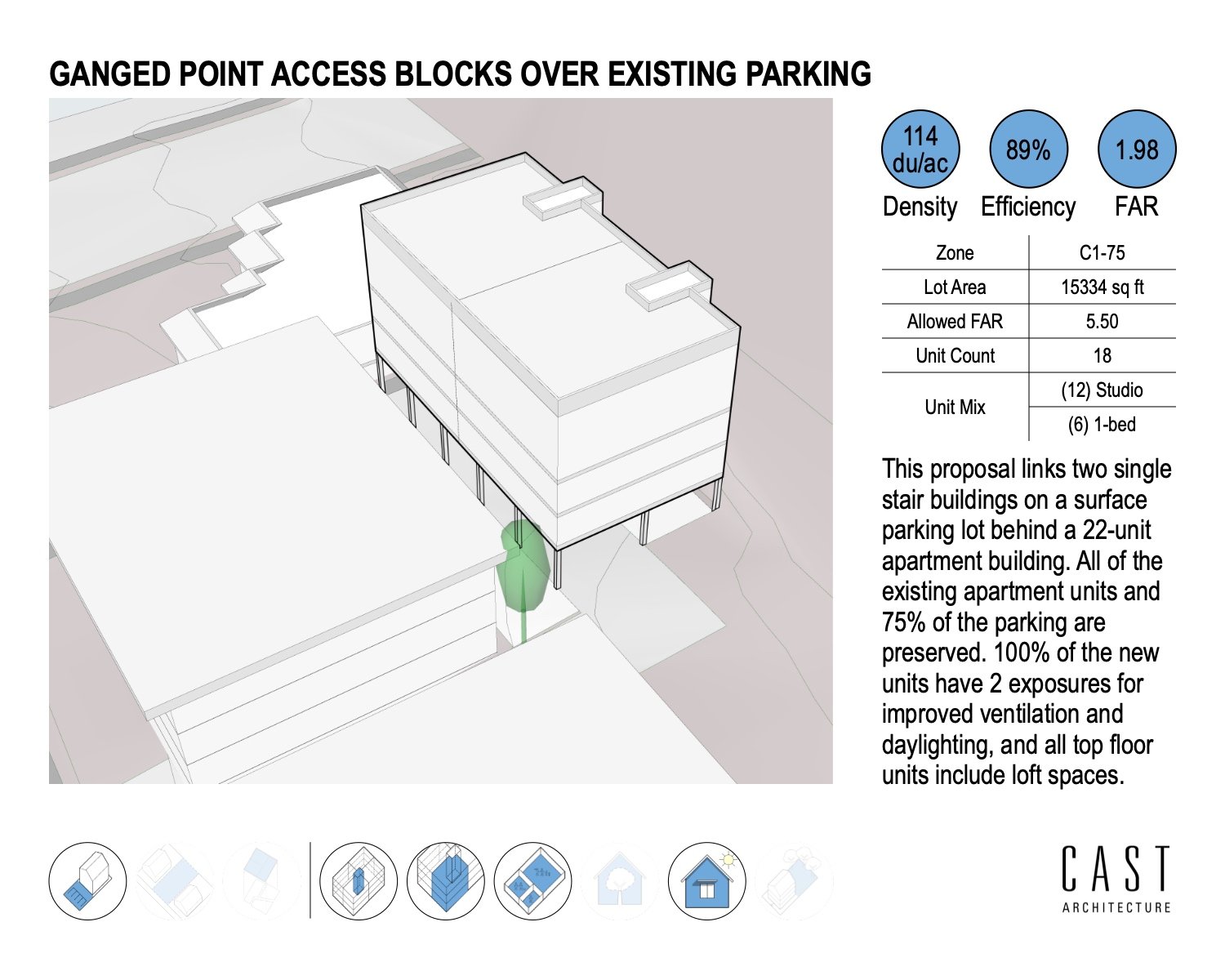
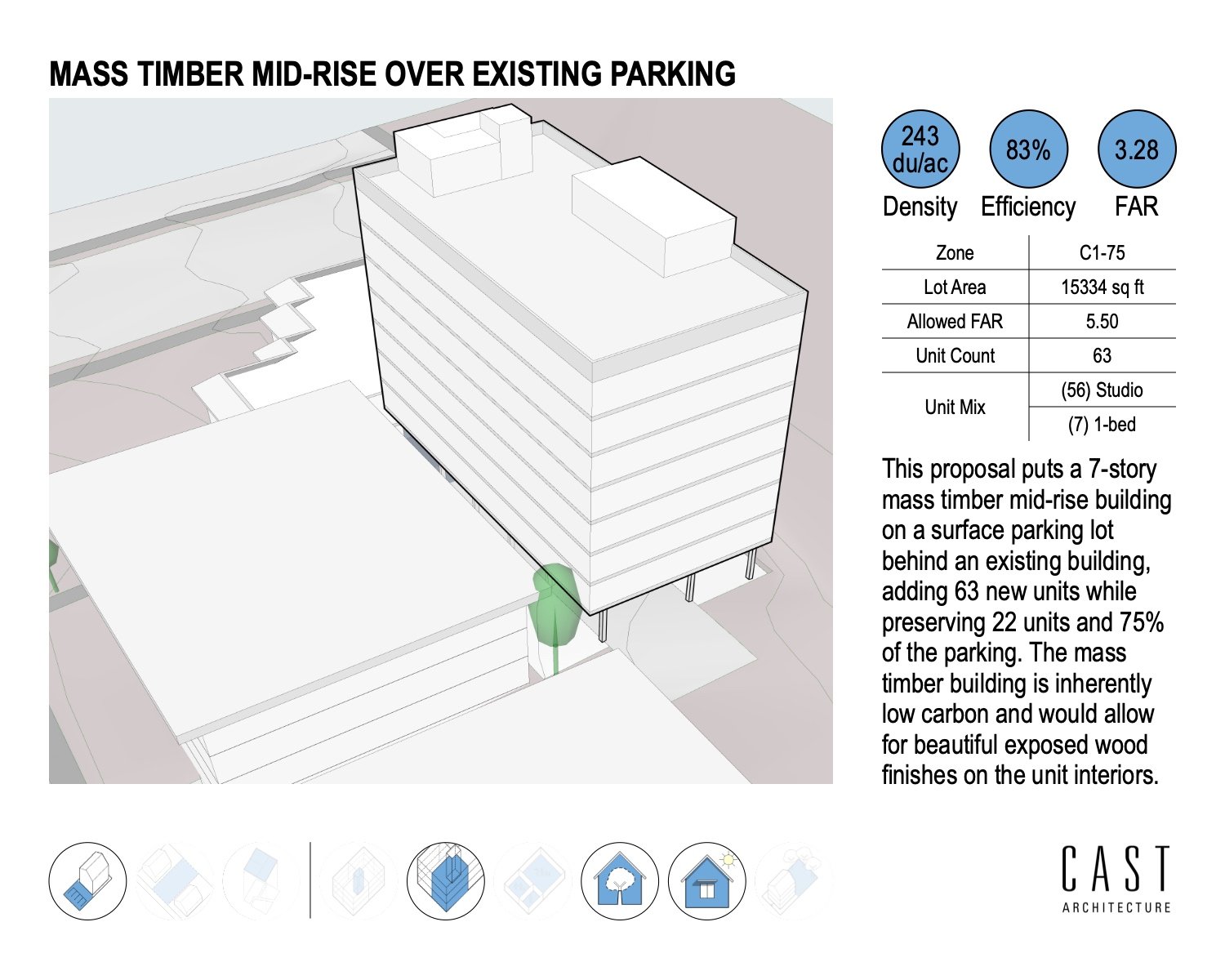
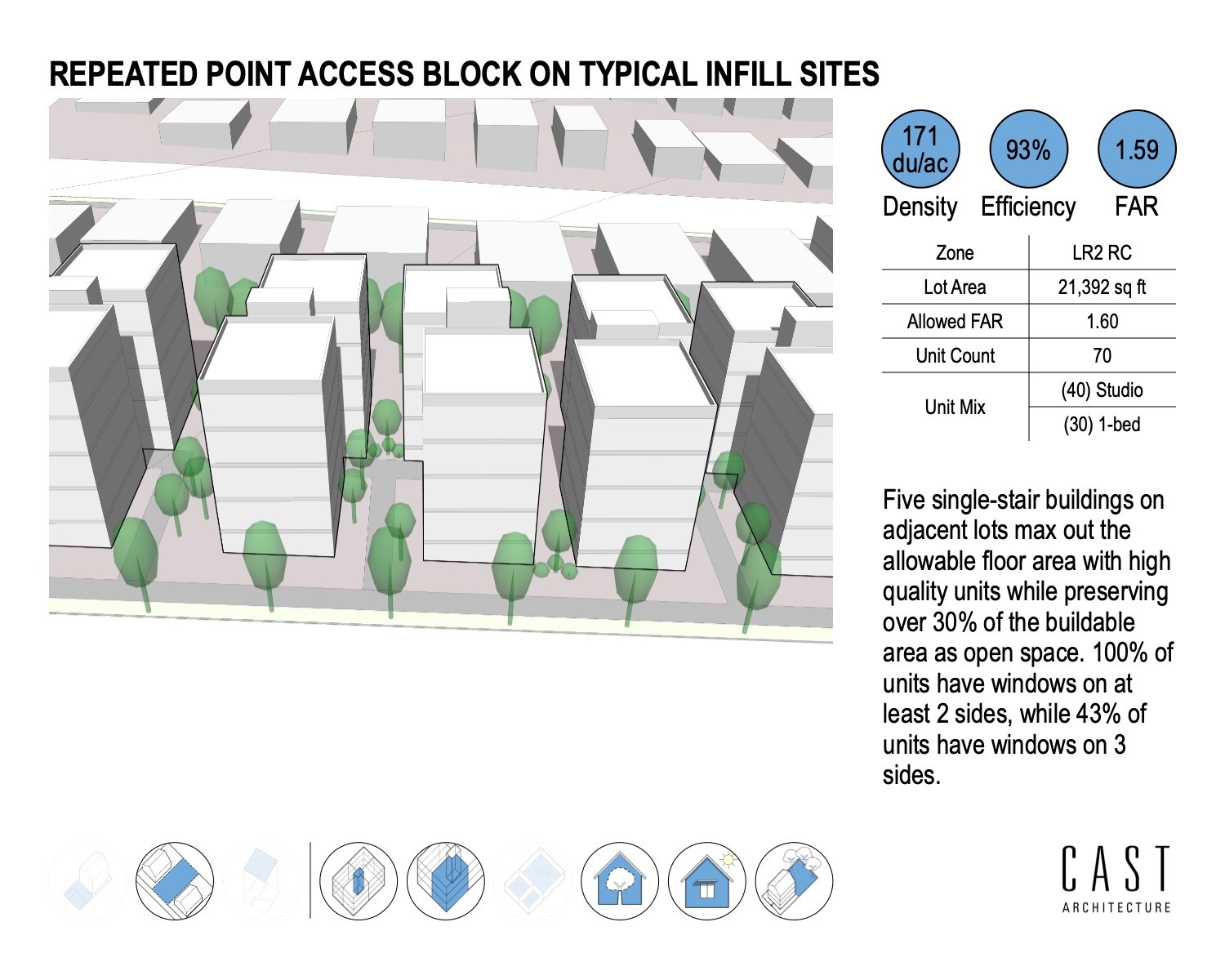
Our design approach and process are thoughtful. We push the limits of sustainability through project performance by setting clear goals and making a positive impact on the environment. Our expertise helps our clients align with their green building goals and understand building life-cycle costs, lower utility bills, enjoy the benefits from natural light, and manage water usage.
The latest climate data tells us that reducing carbon emissions is not enough. To make the biggest impact, we must commit to net zero emissions by 2030—a path that requires strong, immediate action. Since the built environment creates a staggering 40% of the world's emissions, architects, engineers, and owners play a key role. We know that every project can be a catalyst for change.
Our Sustainability Action Plan includes principles and commitments that look for smart, innovative ways to deliver our projects and support climate goals.
Principles
Think Holistically
Act with Urgency
Every Project Counts
Make the Next Project Better
Commitments
Measure Performance
Support Research
Commit to AIA 2030 Challenge
Iterate on Success
Work with Partners
Advocate for Change
Celebrate Wins
See our Sustainability Action Plan here: www.castarchitecture.com/sustainability-action-plan
CAST is dedicated to tracking and reporting our progress toward the AIA 2030 Commitment. We will utilize energy modeling, life cycle assessments, and post-occupancy evaluations to measure operational energy use and embodied carbon across our projects. Our team will document and submit project performance data to the AIA Design Data Exchange (DDx), responding with transparency and accountability. By setting measurable benchmarks and analyzing trends, we will refine our strategies, improve outcomes, and contribute to industry-wide efforts to achieve carbon neutrality. Through this commitment, we will continuously push the boundaries of sustainable design while sharing insights that drive collective progress.
We have had deep roots in sustainable design since our founding in 1999. We are committed to improving the lives of individuals, families, and the community through vibrant and thoughtful design. CAST is at the forefront of sustainable architecture, creating high-performance buildings designed to endure. Our approach prioritizes responsible resource management throughout a building’s lifecycle, integrating climate-responsive design, the best available building science, and site-specific strategies.